The accounting equation Student Accountant Students

The assets on the balance sheet consist of what a company owns or will receive in the future and which are measurable. Liabilities are what a company owes, such as taxes, payables, salaries, and debt. The shareholders’ equity section displays the company’s retained earnings and the capital that has been contributed by shareholders. For the balance sheet to balance, total assets should equal the total of liabilities and shareholders’ equity. The accounting equation is based on the premise that the sum of a company’s assets is equal to its total liabilities and shareholders’ equity.
Example: How to Calculate the Accounting Equation from Transactions
This transaction brings cash into the business and also creates a new liability called bank loan. On the other side of the equation, a liability (i.e., accounts payable) is created. Creditors have preferential rights over the assets of the business, and so it is appropriate to place liabilities before the capital or owner’s equity in the equation. The accounts receivable turnover ratio is a simple formula to calculate how quickly your clients pay. Assets, liabilities, equity and the accounting equation are the linchpin of your accounting system. Your liabilities are any debts your company has, whether it’s bank loans, mortgages, unpaid bills, IOUs, or any other sum of money that you owe someone else.

Accounting Equation Outline
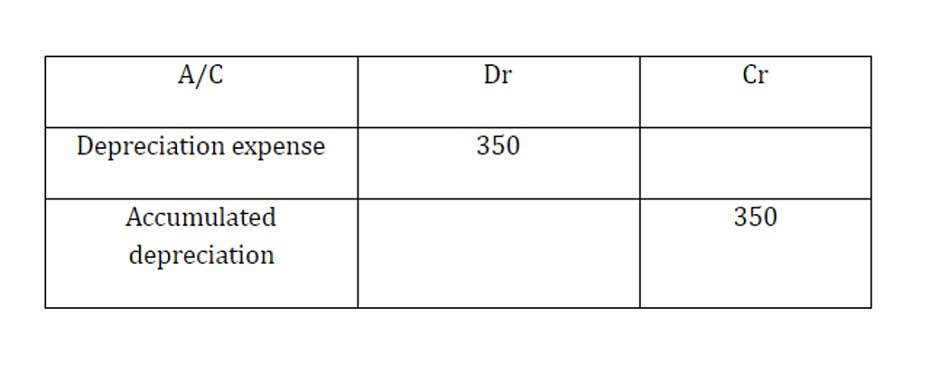
For a sole proprietorship or partnership, equity is usually called “owners equity” on the balance sheet. They include accounts payable, tax payable, accrued expense, note payable, pension fund payable, etc. The assets have been decreased by $696 but liabilities have decreased by $969 which must have caused the accounting equation to go out of balance. To calculate the accounting equation, we first need to work out the amounts of each asset, liability, and equity in Laura’s business.
Effects of Transactions on Accounting Equation
The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets. If a company keeps accurate records using the double-entry system, the accounting equation will always be “in balance,” meaning the left side of the equation will be equal to the right side. The balance is maintained because every business transaction affects at least two of a company’s accounts. For example, when a company borrows money from a bank, the company’s assets will increase and its liabilities will increase by the same amount. When a company purchases inventory for cash, one asset will increase and one asset will decrease.
Accounting Equation
Current assets and liabilities can be converted into cash within one year. Shareholders, or owners of stock, benefit from limited liability because they are not personally liable for any debts or obligations the corporate entity may have as a business. assets equals If we rearrange the Accounting Equation, Equity is equal to Assets minus Liabilities. Net Assets is the term used to describe Assets minus Liabilities. You can think of them as resources that a business controls due to past transactions or events.
Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This is how the accounting equation of Laura’s business looks like after incorporating the effects of all transactions at the end of month 1. In this example, we will see how this accounting equation will transform once we consider the effects of transactions from the first month of Laura’s business. If you’re still unsure why the accounting equation just has to balance, the following example shows how the accounting equation remains in balance even after the effects of several transactions are accounted for. To make the Accounting Equation topic even easier to understand, we created a collection of premium materials called AccountingCoach PRO. Our PRO users get lifetime access to our accounting equation visual tutorial, cheat sheet, flashcards, quick test, and more.
- If the accounting equation is out of balance, that’s a sign that you’ve made a mistake in your accounting, and that you’ve lost track of some of your assets, liabilities, or equity.
- Accountants call this the accounting equation (also the “accounting formula,” or the “balance sheet equation”).
- The assets have been decreased by $696 but liabilities have decreased by $969 which must have caused the accounting equation to go out of balance.
- A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.
- The most liquid asset is cash itself, while non-liquid assets include things such as real estate, machinery, or land because they cannot be converted quickly to cash.
- We can expand the equity component of the formula to include common stock and retained earnings.
What is Double-Entry Accounting?
The capital would ultimately belong to you as the business owner. From an accounting perspective, the showroom cannot show the new vehicle in its accounting books until the day it has gotten control of the asset (i.e., on 5 January 2021). So if a balance sheet of the car showroom is prepared on 31 December 2020, it will not show the new car in the assets because the event that establishes its control over the asset has not occurred by then. However, not all things that provide future economic benefits to a business are to be treated as an asset either in accounting. On 28 January, merchandise costing $5,500 are destroyed by fire. The effect of this transaction on the accounting equation is the same as that of loss by fire that occurred on January 20.
Rearranging the Accounting Equation
- This transaction affects only the assets of the equation; therefore there is no corresponding effect in liabilities or shareholder’s equity on the right side of the equation.
- In the coming sections, you will learn more about the different kinds of financial statements accountants generate for businesses.
- When the total assets of a business increase, then its total liabilities or owner’s equity also increase.
- If the total liabilities calculated equals the difference between assets and equity then an organization has correctly gauged the value of all three key components.
- This includes expense reports, cash flow and salary and company investments.
- For example, ABC Co. started the company on 02 January 2020 by injecting cash into the business of $50,000.
As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets. So, as long as you account for everything correctly, the accounting equation will always balance no matter how many transactions are involved. The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity). Under the accrual basis of accounting, expenses are matched with revenues on the income statement when the expenses expire or title has transferred to the buyer, rather than at the time when expenses are paid. The balance sheet reports the assets, liabilities, and owner’s (stockholders’) equity at a specific point in time, such as December 31.

The accounting equation is also called the basic accounting equation or the balance sheet equation. In accounting, we have different classifications of assets and liabilities because we need to determine how we report them on the balance sheet. The first classification we should introduce is current vs. non-current assets or liabilities. In the above transaction, Assets increased as a result of the increase in Cash. At the same time, Capital increased due to the owner’s contribution. Remember that capital is increased by contribution of owners and income, and is decreased by withdrawals and expenses.
What is the owner’s equity equation in accounting?

We briefly go through commonly found line items under Current Assets, Long-Term Assets, Current Liabilities, Long-term Liabilities, and Equity. These may include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bond issues, warranties, and accrued expenses. Taking time to learn the accounting equation and to recognise the dual aspect of every transaction will help you to understand the fundamentals of accounting. Whatever happens, the transaction will always result in the accounting equation balancing. Anushka will record revenue (income) of $400 for the sale made.

